Domain “Qualified missingness”
Loading Tree…
Definition
Metrics of missing data values that use the coded reasons for missing data.
Explanation
Indicators within this domain make detailed use of the coded reasons for missing data such as refusals, designed jumps or technical defects.
Example
The meaning of computing qualified missingness is illustrated based on the graph below. It depicts an excerpt of an examination and distinguishes three quality levels of coding:
LOW: There are only NA entries to represent missing measurements. For three variables, dementia according to the MMSE an instrument on dementia, job status, and number of births there are many missing values.
INTERMEDIATE: NA’s remain but there are codes for missing data (999, 998)
HIGH: All missing values have been assigned a code to explain reasons about missingness. Most of the missing values were due to permitted jumps and are only missing by design. The item was not assessed based on design and therefore should not be treated as missing.
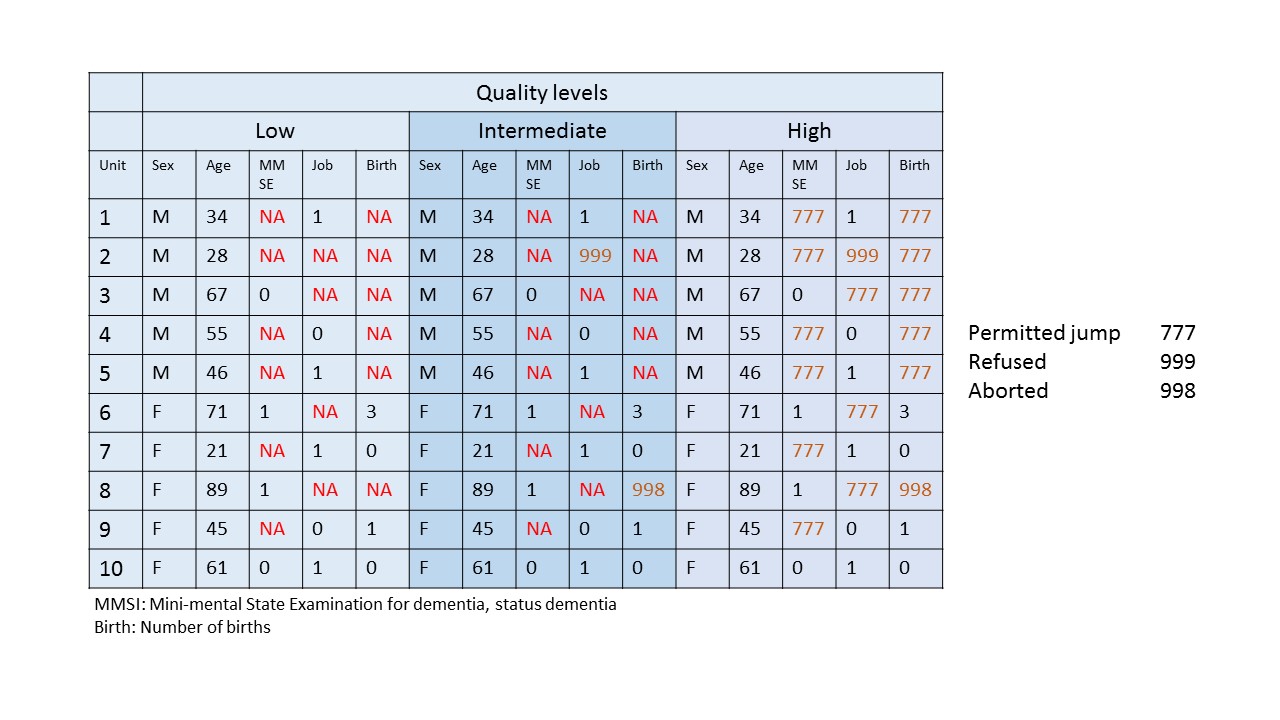
For low and intermediate quality coding’s there remain ambiguities as to the interpretation of missing values and the domain crude missingness applies. In the high quality column there are valid data values for data fields. This allows for detailed assessments on the structure and meaning of missing data as defined in the domain qualified missingness.
Guidance
The proper computation of qualified missingness indicators requires a complete representation of missing values by user defined value codes with an unambiguous meaning. If this precondition is not met, crude missingness assessments should preferably be conducted instead.
After computing qualified missingness indicators, it must be secured that numerical missing values are no longer treated as numerical values in subsequent analyses. If necessary an appropriate recoding should take place.
Literature
The American Association for Public Opinion Research. Standard Definitions: Final Dispositions of Case Codes and Outcome Rates for Surveys. 2016. AAPOR. https://www.aapor.org/AAPOR_Main/media/publications/Standard-Definitions20169theditionfinal.pdf.
Stausberg, J., D. Nasseh and M. Nonnemacher (2015). “Measuring data quality: A review of the literature between 2005 and 2013.” Stud Health Technol Inform 210: 712-716.



