Indicator “Unexpected association direction”
Loading Tree…
Definition
The observed direction of an association (e.g. negative, positive) deviates from the expected direction.
Explanation
Associations of data elements may be negative, positive, or such data elements may be completely unrelated. In case of expected strong associations the false sign of the association coefficient indicates an unexpected association direction.
Example
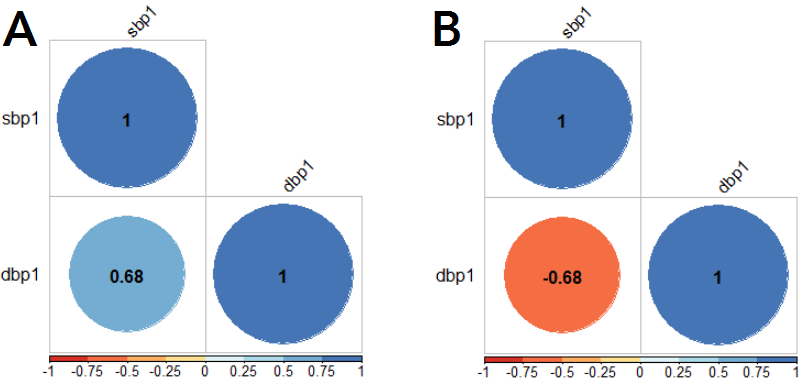
Measurements of systolic and diastolic blood pressure should show a positive correlation. In the Figure below (panel A) such an expected association direction is shown. In panel B of this figure the strength of association is similar but the direction differs.
Guidance
Associations between data elements can be manifold and are not
restricted to associations of numerical/continuous data elements. The
visual check of an association direction provides descriptive insights
into deviations from expected patterns. An introduction to mining
association rules is given by
Hahsler et al. 2018 for the R
package arules. Choosing the correct test for associations
is discussed in
Gonzalez-Chica et al. 2015.
Interpretation
A inverse association direction indicates errors in the data. Causes for such deviations are manifold such as false sign operation, transformation of measurements, or false use of instruments and/or devices.
Descriptors
Literature
Hahsler, M., et al. “Introduction to arules-A computational environment for mining association rules and frequent item sets, 2010.” (2018).
Gonzalez-Chica, David Alejandro, et al. “Test of association: which one is the most appropriate for my study?.” Anais brasileiros de dermatologia 90.4 (2015): 523-528.



