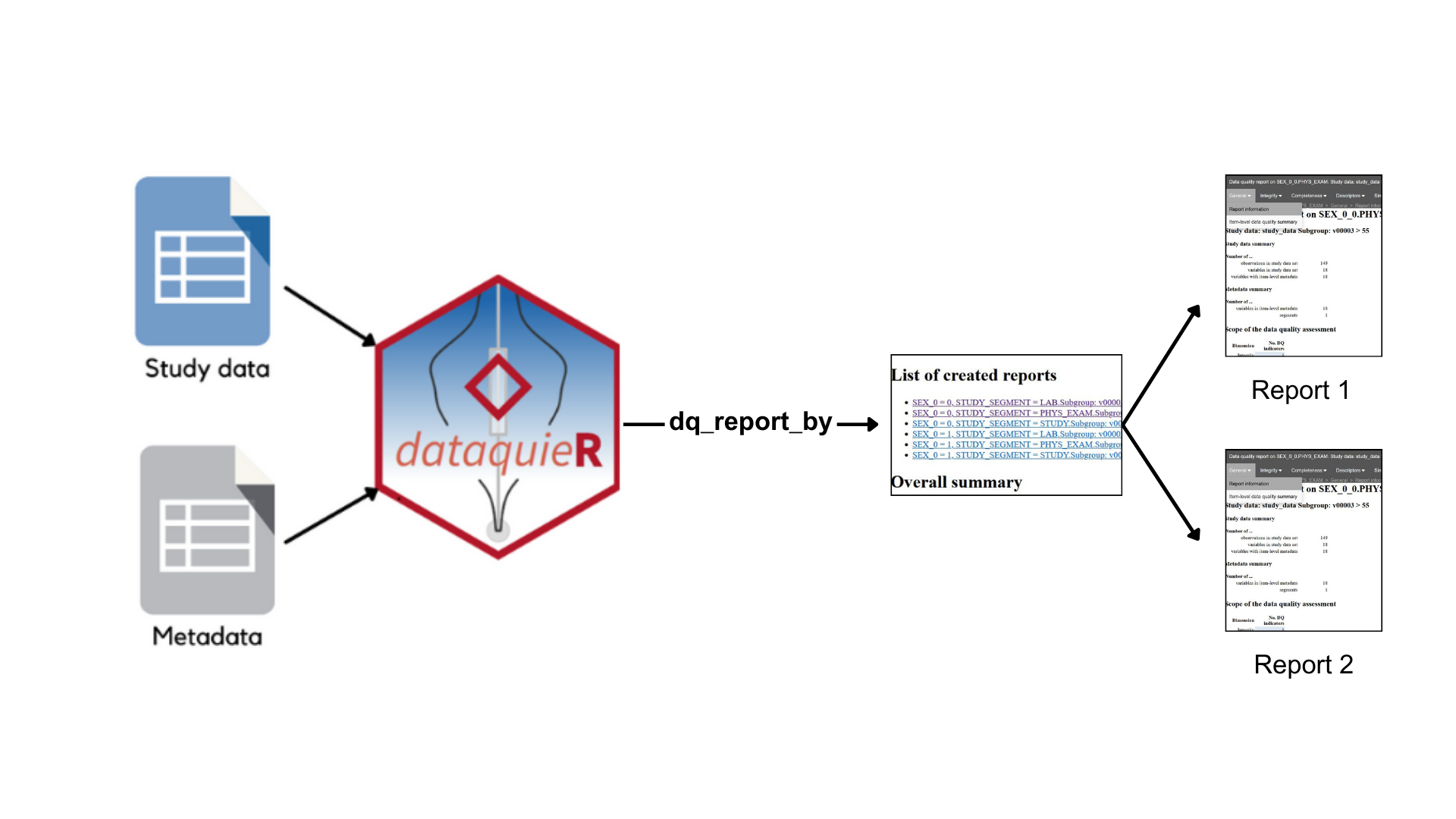
How to create multiple reports with one function: dq_report_by
Several automated data quality assessments can be created
simultaneously using the function dq_report_by from the R
package dataquieR. This tutorial informs on how to specify the criteria
for splitting the data in several reports, as well as the definition of
the needed study data (i.e., the collected data) and
metadata (i.e., information and requirements about the
study data).
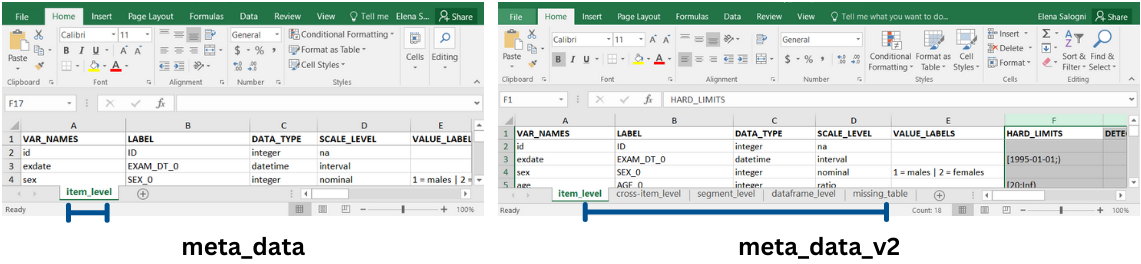
Metadata
The function dq_report_by can use multiple
levels metadata that can be specified in 2 ways:
in an Excel workbook with multiple spreadsheets containing metadata organized in several tables. These spreadsheets are named following dataquieR conventions: “item_level”, “cross-item_level”, “segment_level”, “dataframe_level”, “item_computation_level”. This type of metadata is identified by the function argument
meta_data_v2as separate metadata using the following function arguments:
meta_data, for the “item_level” metadata;meta_data_segment, for the “segment_level” metadata;meta_data_dataframe, for the “dataframe_level” metadata;meta_data_cross_item, for the “cross-item_level” metadata;meta_data_item_computation, for the “item_computation_level” metadata;missing_tables, for the table/s containing the missing codes.
Study data
Study data can be provided in two main ways in this function.
1. Study data specified using the argument
study_data
The argument study_data can be used to specify one table
or multiple tables containing the collected data. They can be specified
using:
a path containing the file name and the file extension
study_data = "~/Desktop/sd1.xlsx", ...And in case of multiple files, it can be a vector of several paths
study_data = c("~/Desktop/sd1.xlsx","~/Desktop/sd2.xlsx"), ...a URL
study_data = "https://.../study_data.xlsx", ...an object in R
study_data = sd1, ...just the file name and the extension
In this case another argument
input_diris mandatory to state where the file is located.study_data = "study_data.xlsx", input_dir = "~/Desktop/data/", ...just the table name
This is a special case that works only with study data and metadata examples available from the dataquieR website.
study_data = "study_data" #for the synthetic examplestudy_data = "ship" #for the SHIP-based example
2. Study data specified in the “dataframe_level” metadata.
In this case the study_data argument is not used and the
only table or several tables containing the data are listed in the
dataframe_level metadata, in the column
DF_NAME, a row per table, as in the following example.
| DF_NAME | DF_ELEMENT_COUNT | DF_ID_VARS |
|---|---|---|
| ~/Desktop/data/sd1.csv | 10 | v00001 |
| ~/Desktop/data/sd2.xlsx | 12 | v00001 | ID |
| https://exampleURL/data/sd3.xlsx | 20 | v00001 |
If you want to provide only the table name and the extension in the
dataframe_level metadata (as in the following example),
then the additional argument input_dir is mandatory.
input_dir = "~/Desktop/data/", ...
| DF_NAME | DF_ELEMENT_COUNT | DF_ID_VARS |
|---|---|---|
| sd1.csv | 10 | v00001 |
| sd2.xlsx | 12 | v00001 | ID |
Storage of results
Resulting data quality reports can be stored in 2 ways.
1. Reports are available in R, in the Viewer panel.
The reports can be available inside R, in the Viewer panel. From there they can be opened in a browser. This is achieved using the argument:
also_print = FALSE
2. Reports are saved in a folder.
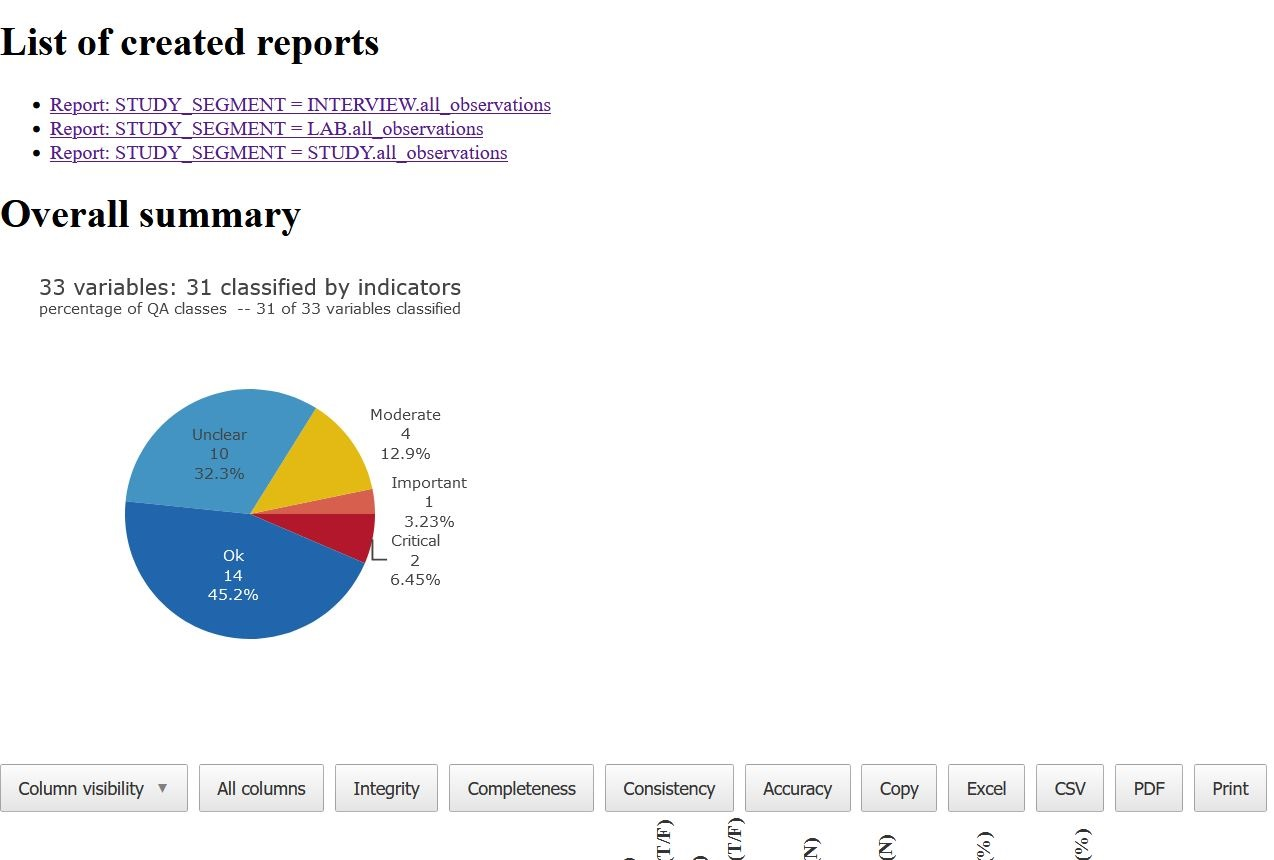
Reports can be saved in a folder on your device. In this case an
overview page containing a list of all created reports and the main data
quality issue summary is provided. To save the reports in a folder (for
example “Reports_july”), two arguments are needed,
also_print set on TRUE and output_dir to
define the folder to create and its path (Note: the folder can not exist
already):
also_print= TRUE, output_dir = "~/Desktop/Reports_july/", ...
You will have then a new folder “Reports_july” containing all the
reports. To open the overview page with the link to all the reports, you
will have to click on index.html. Here is an example of how
the overview page appears.
Create multiple reports using the synthetic data example: a basic example
Using the arguments listed up to now, it is possible to create multiple reports. By defaults if nothing is specified about how to separate data in several reports, the column “STUDY_SEGMENT” in the item_level metadata is automatically used.
Note: You can also decide that you do not want any
separation and obtain a unique report using
segment_column = NULL.
Here is an example with the synthetic data of
dataquieR.
dq_report_by(
study_data = "study_data",
meta_data_v2 = "meta_data_v2",
output_dir = "/REPORT_by_synthetic_data/",
also_print = TRUE,
dimensions = "Completeness")This will create 5 reports, one per STUDY_SEGMENT in the
item_level metadata.
Attention: The argument
dimensions = "Completeness" limits the report to the
Integrity and Completeness dimensions (review concept at this link), and the descriptive
statistics. To obtain complete reports (including all possible
dimensions) the argument need to be set to null or “all”:
dimensions = NULL or dimensions = "all"
Create multiple reports defining the desired split using the synthetic data example
Other arguments are available to define the reports to create.
Define split based on a column in the item_level metadata
To define how the data are separated in several reports, there are the following arguments:
segment_column: name of an item_level metadata attribute (i.e., column) usable to create reports for groups of variables, e.g., Blood_test, Body_measurements. By default, reports are created based on the content ofSTUDY_SEGMENT, if nothing is specified. Here is an example:segment_column = "STUDY_SEGMENT"orsegment_column = "REPORT_NAME"segment_select: if given, the reports are not created based on all levels ofsegment_column, but only for the content of this vector. A character vector or a regular expression (e.g., “.*_EXAM$“) can be provided. This argument can not be used if nosegment_columnis provided. Here is an example:segment_select = c("STUDY", "LAB")orsegment_select = "STUDY | LAB"segment_exclude: if given, the reports are not created based on all levels ofsegment_column, but only for the levels that are not stated in this vector. A character vector or a regular expression (e.g., “.*_EXAM$“) can be provided. It can only be specified if asegment_columnis present. Here is an example:segment_exclude = "^INT"orsegment_exclude = c("STUDY", "INTERVIEW")orsegment_exclude = "STUDY | LAB"
Note: There is only one exception in which both
segment_select and segment_exclude can be used
without specifying segment_column and it happens only when
using levels of the column STUDY_SEGMENT.
Define split based on a column in the study data
To define how the data are separated in several reports, there are the following arguments:
strata_column: name of a study variable containing categories usable to separate the reports, e.g. the study centers. Both labels andVAR_NAMESare accepted. In case of NAs in the selected variable, a separate report containing the NAs subset will be created. Here is an example:strata_column = "SEX"strata_select: if given, the categories of strata_column usable to create reports are limited to the content of this vector. A character vector or a regular expression can be provided (e.g., “^a.*$“). This argument can not be used if no strata_column is provided. Here is an example:strata_select = "males | females"strata_exclude: if given, the reports are not created based on all categories ofstrata_column, but only for the categories that are not stated in this vector. Here is an example:strata_exclude = "1"selection_type: this argument is optional and can be used to specify if you wrote an actual value (“value”), a value_label (“v_label”), or a regular expression (“regex”) instrata_selectorstrata_exclude. Here is an example:strata_exclude = "females", selection_type = "v_label",
Define a subgroup of data to use from the study data
It is possible to refine the selection of observational units, for example selecting only adults, or individuals taller than 170cm, using the argument:
subgroup: if given, it can be used to define subgroups of cases, using REDCap rules. For example, it can be used in case you want to limit the reports to individuals of a certain age. For examplesubgroup = "[v_age] > 30"
All previous arguments can be combined. So for example, using the synthetic example data you can decide to create complete reports for two study segments (“INTERVIEW” and “LAB”), only for females of age greater than 50. The code will be as follows:
dq_report_by(
study_data = "study_data",
meta_data_v2 = "meta_data_v2",
output_dir = "~/Desktop/REPORT_by_synthetic_data_v2/",
also_print=TRUE,
dimensions = NULL,
segment_column = "STUDY_SEGMENT",
segment_select = c("INTERVIEW", "LAB"),
strata_column = "SEX_0",
strata_select = "females",
selection_type = "v_label",
subgroup = [v00003] > 30)Specify group of variables
Limit reports creation to a group of variables
Reports can be limited to a set of variables using the argument
resp_vars. The reports will be created only using that
variables from the study data. The function is capable of retaining all
the referred variables needed to assess the variables indicated. These
referred variables remain in the metadata but they will not be part of
the data quality assessment. Here is an example on how to create a
report using only the six variables indicated.
dq_report_by(
resp_vars = c("CENTER_0", "PSEUDO_ID",
"SBP_0", "DBP_0",
"CRP_0", "BSG_0"),
study_data = "study_data",
meta_data_v2 = "meta_data_v2",
output_dir = "~/Desktop/REPORT_by_synthetic_data_v3/",
also_print=TRUE,
dimensions = NULL,
segment_column = "STUDY_SEGMENT")Specify variables containing ID
In case of absence of the dataframe_level metadata,
it is possible to specify which variables contain the information about
the ID (useful in case of multiple data frames that need to be
combined). The argument to specify the ID variables is
id_vars. For example id_vars = "v_id"



