Logical or empirical contradictions
To assess the consistency of different data elements, we apply the
function con_contradictions_redcap(). The rules to identify
contradictions must first be defined in the cross-item metadata. An
overview is given in the respective tutorial.
Each line within the spreadsheet defines one rule. Subsequently, the
contradictions assessment may be triggered using the table as the point
of reference:
# Load dataquieR
library(dataquieR)
# Load data
sd1 <- prep_get_data_frame("ship")
# Load metadata
prep_load_workbook_like_file("ship_meta_v2")
meta_data_item <- prep_get_data_frame("item_level") # item_level is a sheet in ship_meta_v2.xlsx
meta_data_cross_item <- prep_get_data_frame("cross-item_level") # cross-item_level is another sheet in ship_meta_v2.xlsx
# Apply indicator functions
AnyContradictions <- con_contradictions_redcap(
study_data = sd1,
meta_data = meta_data_item,
label_col = "LABEL",
meta_data_cross_item = meta_data_cross_item,
threshold_value = 1
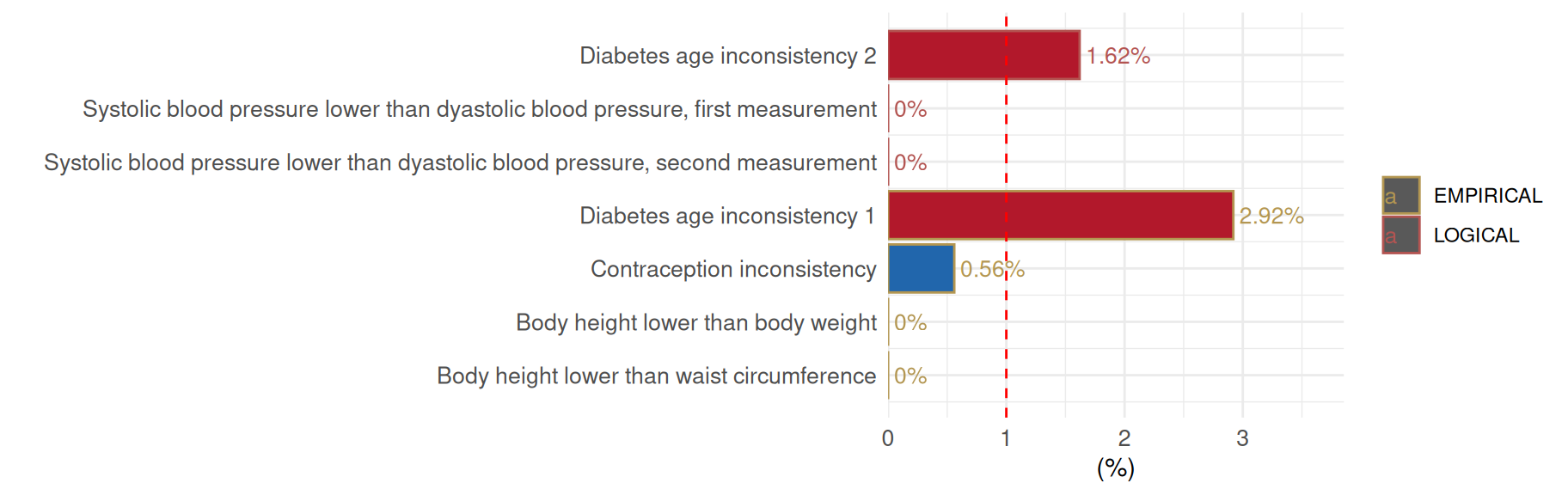
)A summary table shows the number and percentage of contradictions for each defined rule:
AnyContradictions$VariableGroupData| Check | Contradiction Type | Contradictions (Number) | Contradictions (Percentage (0 to 100)) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | Diabetes age inconsistency 2 | LOGICAL | 35 | 1.62% |
| 1 | Systolic blood pressure lower than dyastolic blood pressure, first measurement | LOGICAL | 0 | 0% |
| 2 | Systolic blood pressure lower than dyastolic blood pressure, second measurement | LOGICAL | 0 | 0% |
| 6 | Diabetes age inconsistency 1 | EMPIRICAL | 63 | 2.92% |
| 5 | Contraception inconsistency | EMPIRICAL | 12 | 0.56% |
| 3 | Body height lower than body weight | EMPIRICAL | 0 | 0% |
| 4 | Body height lower than waist circumference | EMPIRICAL | 0 | 0% |
In this example, rule seven leads to the identification of 35 contradictions: age of onset for diabetes is provided (DIAB_AGE_ONSET_0), but the variable on the presence of diabetes (DIABETES_KNOWN_0) does not indicate a known disease.
The distributions may also be displayed as a plot:
AnyContradictions$SummaryPlot